Lipoma Treatment Solutions: What You Need to Know
- dynamic clinic
- Oct 2, 2024
- 4 min read
Lipomas are benign tumors composed primarily of fat tissue, and they are among the most common soft tissue tumors found in adults. Typically painless and slow-growing, lipomas can occur anywhere in the body, most often on the back, neck, arms, and thighs. While they are generally harmless, some people choose to seek treatment for cosmetic reasons or if the lipoma becomes painful or bothersome. Understanding the available treatment options can help you make informed decisions regarding your health. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Lipoma Treatment in Dubai solutions and what you need to know.
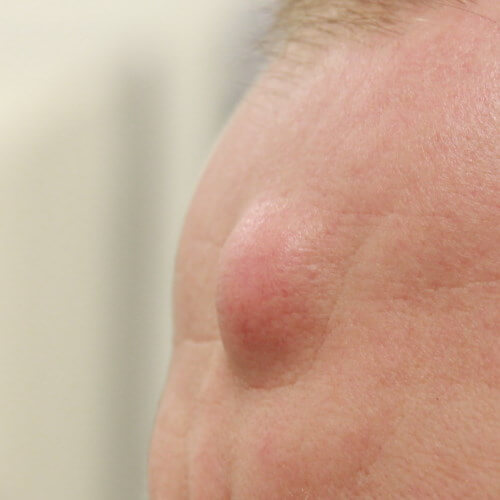
What Are Lipomas?
Definition and Characteristics
A lipoma is a soft, rubbery lump that forms beneath the skin. Lipomas are usually:
Soft to the Touch: They can be easily moved under the skin when pushed.
Painless: Most lipomas do not cause pain or discomfort, although larger ones may press on surrounding tissues and nerves, leading to discomfort.
Slow-Growing: Lipomas typically grow slowly and may remain small for years.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of lipomas is not fully understood. However, some factors that may increase the risk of developing lipomas include:
Genetics: A family history of lipomas may predispose individuals to developing them.
Age: They are most commonly found in adults, particularly those between the ages of 40 and 60.
Obesity: Although lipomas can occur in people of any weight, some studies suggest a link between obesity and an increased likelihood of developing lipomas.
Symptoms
While lipomas are often asymptomatic, individuals may notice the following signs:
A soft lump beneath the skin that can be easily moved.
A gradual increase in size over time.
Discomfort if the lipoma presses on nearby structures.
Treatment Options for Lipomas
The treatment for lipomas largely depends on the individual's symptoms, the size of the lipoma, and personal preference. Here are the most common treatment options:
1. Watchful Waiting
In many cases, especially for small, asymptomatic lipomas, a watchful waiting approach may be recommended. Regular monitoring allows for tracking any changes in size or symptoms. If the lipoma remains unchanged and does not cause discomfort, treatment may not be necessary.
2. Surgical Excision
Surgical removal is the most definitive treatment for lipomas and is often recommended for those that are painful, growing, or causing cosmetic concerns. The procedure typically involves:
Local Anesthesia: The area surrounding the lipoma is numbed to minimize discomfort.
Incision and Excision: A small incision is made over the lipoma, and it is carefully excised from the surrounding tissue.
Closure: The incision is then closed with sutures.
Surgical excision usually leads to immediate relief and a low risk of recurrence, making it a preferred option for many patients.
3. Liposuction
Liposuction is a minimally invasive technique used to remove lipomas, especially smaller ones. This method involves:
Local Anesthesia: The area is numbed for comfort.
Cannula Insertion: A small incision is made, and a thin tube (cannula) is inserted into the lipoma.
Fat Removal: The fatty tissue is suctioned out through the cannula.
While liposuction can effectively remove lipomas, it may not be suitable for all cases, particularly larger lipomas. Additionally, there may be a risk of recurrence with this method.
4. Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections have been studied as a non-surgical treatment option for lipomas. This approach involves injecting a corticosteroid solution directly into the lipoma, which may help reduce inflammation and shrink the growth. However, this treatment is not always effective and may not lead to complete resolution.
5. Alternative Treatments
Some alternative treatments are occasionally considered for lipoma management, though scientific evidence supporting their efficacy is limited:
Home Remedies: Natural remedies, such as apple cider vinegar or turmeric, are sometimes touted for their potential to reduce lipoma size. However, these remedies lack substantial scientific backing, and it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any home treatments.
Dietary Changes: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and fiber may support overall health. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains could be beneficial in managing body fat, but their direct effect on lipomas remains unclear.
Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs, like dandelion root and burdock root, are believed to support fat metabolism and may be considered by some. However, their effectiveness for lipomas is not well-documented.
6. Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes can contribute to overall health and may help manage lipomas. Consider the following strategies:
Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week. Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and improve circulation.
Balanced Diet: Incorporate nutrient-rich foods and limit processed foods high in sugars and unhealthy fats. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can promote overall well-being.
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated supports bodily functions and aids in detoxification. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact overall health, so practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
When to Seek Treatment
Although lipomas are generally harmless, there are certain circumstances in which individuals should seek medical advice:
Rapid Growth: If a lipoma grows quickly or changes in appearance, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to rule out other conditions.
Pain or Discomfort: If the lipoma becomes painful, tender, or interferes with daily activities, treatment options should be discussed.
Cosmetic Concerns: If the appearance of a lipoma affects self-esteem or confidence, exploring treatment options for aesthetic improvement may be beneficial.
Conclusion
Lipomas are benign growths that often do not require treatment unless they cause discomfort or concern. When intervention is necessary, options range from surgical excision and liposuction to corticosteroid injections. Alternative treatments and lifestyle modifications may also play a role in managing lipomas.
As with any medical condition, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment recommendations. Understanding your treatment options can help you take control of your health and make informed decisions regarding lipoma management.




Comments